
How to Find and Fix Non-Indexed Pages: Step-by-Step Guide
Ensuring that all valuable pages on your website are indexed by search engines is crucial for maximizing organic traffic and conversions. Non-indexed pages are invisible to Google, meaning your content, products, or services may never reach potential users. In this guide, we’ll show you how to find and fix non-indexed pages efficiently, step by step.
Step 1: Identify Non-Indexed Pages
Before fixing anything, you need to know which pages aren’t indexed. You can use multiple tools and methods:
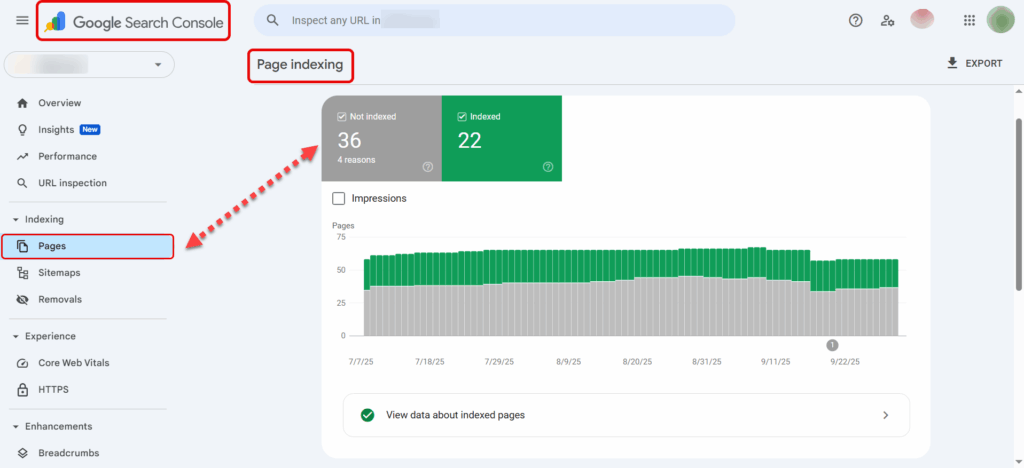
Google Search Console (GSC)
Go to Coverage > Excluded to see pages that Google has discovered but not indexed.
Common reasons in GSC: Discovered, currently not indexed, Crawl anomaly, Duplicate without user-selected canonical.
Site Search Operator
- Use site:yourdomain.com in Google to see which pages are indexed.
- Compare with your full sitemap to find missing URLs.
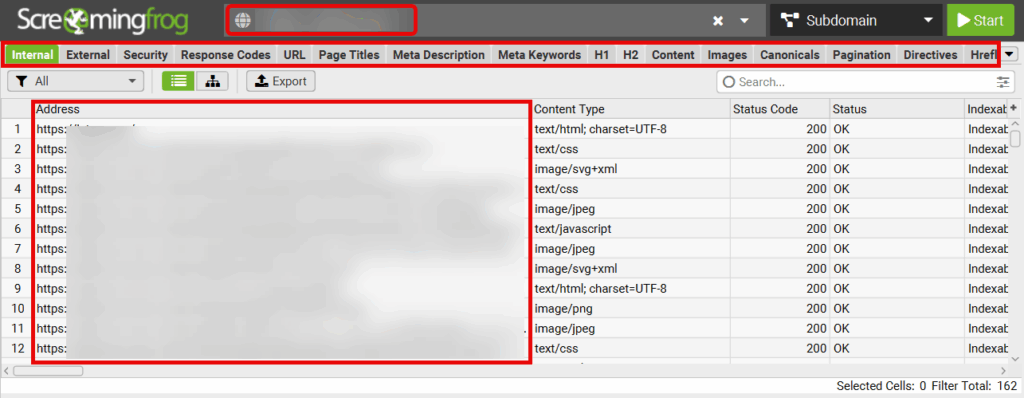
Screaming Frog or Site Crawlers
Crawl your site to list all pages.
Export URLs and compare them with indexed pages from GSC.
Pro Tip: Document all non-indexed URLs in a spreadsheet for easy tracking.
NOTICE: You can easily identify and fix these issues with the jetseopro . This advanced platform allows SEO professionals to quickly detect non-indexed pages, broken links, duplicate content, and other technical problems that may affect your site’s performance. With a user-friendly dashboard, automated audits, and actionable insights, you can streamline your SEO workflow and ensure all important pages are properly indexed by Google.
jetseopro is designed to save time, reduce manual work, and help you maintain full control over your site’s SEO health. Whether it’s fixing indexing problems, improving internal linking, or monitoring page performance, this tool provides everything you need in one powerful platform.
Step 2: Diagnose Why Pages Aren’t Indexed
After identifying the non-indexed pages, check why Google is not indexing them. Common causes include:
Noindex meta tag: Check
- Blocked by robots.txt: Ensure pages aren’t blocked in robots.txt.
- Duplicate content: Google may skip pages that are too similar to others.
- Low-quality or thin content: Pages with very little content may not be indexed.
- Canonical errors: Ensure canonical tags point to the correct URL.
- Server or technical errors: Check for 400, 500, or slow-loading pages.
Quick Access:
locked by robots.txt → Check robots.txt → Allow important pages
Duplicate content → Identify similar pages → Consolidate or use correct canonical
Low-quality / thin content → Improve content → Add text, images, internal links
Canonical errors → Verify canonical tags → Correct URL if needed
Server / technical errors → Check 400/500 errors → Fix redirects & improve page speed
Step 3: Fix Non-Indexed Pages
Once you identify the cause, apply the right fix:
- Remove Noindex Tags
- If a page should be indexed, remove any .
- Re-submit the page to Google via GSC.
- Update robots.txt
- Make sure important pages are not blocked.
- Use Allow: /path/ for critical sections.
- Fix Duplicate or Thin Content
- Consolidate similar pages or add unique content.
- Use canonical tags correctly if multiple versions exist.
- Improve Page Quality
- Add detailed text, images, infographics, and internal links.
- Make the page useful for the user (EEAT-compliant).
- Resolve Technical Issues
- Fix 404, 500, and redirect chains.
- Ensure fast page load and mobile-friendly design.
- Internal Linking
- Link from high-authority pages to non-indexed pages.
- Internal links help Google discover and index pages faster.
Step 4: Request Indexing in Google Search Console
After fixing issues:
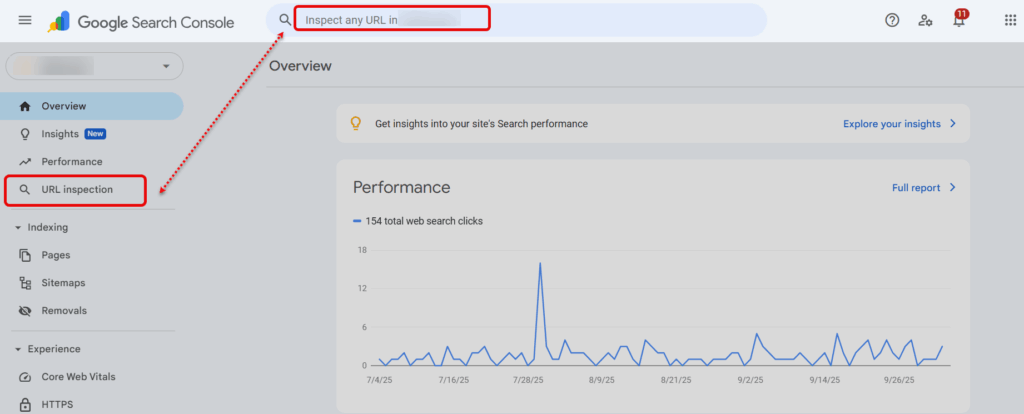
- Go to GSC > URL Inspection Tool.
- Paste the URL and click Request Indexing.
- Monitor the status; Google usually indexes pages within a few days to a couple of weeks.
- Tip: Prioritize pages with high SEO value or strategic importance
Pages are usually indexed by Google within a few days to a couple of weeks. If you have any questions about SEO or want to learn best practices, check out Google Search Central. This site is Google’s official resource for webmasters and SEO professionals, offering guides, tips, and tools to help improve your site’s visibility and performance in search results.
Step 5: Monitor and Prevent Future Non-Indexation
- Regularly Audit: Use GSC and site crawlers monthly.
- Update Sitemaps: Ensure all important URLs are listed in XML sitemaps.
- Monitor Analytics: Check traffic drops to detect indexation issues.
- Internal Linking Strategy: Ensure every key page is linked from multiple relevant pages.
Is there a difference in indexing speed between new vs. old domains?
Usually. Established, authoritative domains tend to get indexed faster than brand-new sites. Building site authority improves indexing speed.
Can international or geo-targeted pages face special indexing issues?
For multi-language or geo-targeted pages, use hreflang tags, local schema, and country-specific sitemaps to ensure proper indexing.
How do I prevent non-indexed pages from accumulating in the future?
Maintain regular audits, proper internal linking, XML sitemaps, and high-quality content to keep all important pages indexed.
Can non-indexed pages affect my overall SEO performance?
Definitely. Non-indexed pages reduce organic visibility, link equity, and content reach, which can negatively impact SEO.
What’s the best way to prioritize fixing high-value non-indexed pages?
Focus on pages that drive traffic, conversions, or rankings. High-priority pages should be fixed and submitted first.
Can structured data or schema help pages get indexed faster?
Yes. Structured data helps Google understand content context, improving the chance of faster indexing and eligibility for rich results.
Conclusion
Non-indexed pages can silently hurt your SEO performance. By finding and fixing non-indexed pages systematically, you ensure all your valuable content is discoverable, authoritative, and optimized for search engines. Use Google Search Console, technical audits, content improvements, and internal linking to maintain full index coverage.
Why are some of my pages not showing up in Google search results?
Pages may not be indexed due to noindex tags, robots.txt restrictions, thin content, duplicate content, or technical errors like 404 or 500 status codes.
How can I quickly find all non-indexed pages on my website?
Use Google Search Console (Coverage > Excluded), site search operators (site:yourdomain.com), or a crawling tool like Screaming Frog to identify non-indexed pages.
What tools can help me identify pages that Google hasn’t indexed?
Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, SEMrush, JETSEO TOOLS and other website crawlers are effective for detecting non-indexed URLs.
How long does it take for Google to index new or fixed pages?
Typically, indexing can take a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the site authority, crawl budget, and page importance.
Can a noindex tag or robots.txt block a page from being indexed?
Yes. Noindex meta tags explicitly tell Google not to index a page, and robots.txt can prevent crawling, which indirectly prevents indexing.
How do I fix non-indexed pages caused by duplicate content?
Consolidate similar pages, use canonical tags correctly, or rewrite content to be unique and valuable for users.
Can slow loading speed or technical errors prevent indexing?
Absolutely. Pages with 404/500 errors, redirect chains, or very slow loading times may be ignored by Google.
How important is internal linking for getting pages indexed?
Very important. Strong internal linking from high-authority pages helps Google discover and index pages faster.
Does thin content or low-quality content prevent indexing?
Yes. Pages with very little content or low user value are often not indexed. Enhancing content quality is key.
Should I use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console for each page?
For high-value pages or fixed non-indexed pages, use the URL Inspection Tool to request indexing after resolving issues.
How do canonical tags affect page indexing?
Canonical tags tell Google which version of a page to index. Incorrect canonicalization can prevent indexing of important pages.
Can sitemap errors or missing pages cause non-indexation?
Yes. Ensure your XML sitemap includes all important URLs and is submitted to Google Search Console.
Are there differences in indexing for desktop vs. mobile pages?
Google primarily uses mobile-first indexing, so mobile accessibility, responsiveness, and load speed impact indexing.
How do I monitor indexing status over time for large websites?
Use Google Search Console reports, crawling tools, and automated monitoring to track which pages are indexed and which are not.